Spatial resolution is vital in Raman microscopy for discriminating different structures in a sample.
The better the spatial resolution, the more detailed information can be gained. For example, differentiating different components in a single cell or detecting defects in graphene materials.
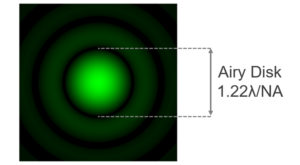
There are two main factors that determine the lateral (XY plane) resolution in a Raman microscope: the excitation wavelength (λ) and,
the numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens used. There a several definitions of lateral spatial resolution but the most commonly used is:
For example, using a 405 nm laser and an objective with a NA of 0.9 the theoretical spatial resolution achievable is 275 nm. However it should be stressed that this is a theoretical ideal. It is rarely achieved in practice due to sample dependent scattering properties. A practical Raman spatial resolution is on the order of 1 µm.
Since the spatial resolution is proportional to laser excitation wavelength, shorter wavelength lasers can be be used to achieve higher spatial resolution. Raman Microscopes are often equipped with multiple laser wavelengths, enabling the user to find the best compromise between required spatial resolution and other constraints such as fluorescence from the sample.
The numerical aperture is determined by the type of objective lens used. Standard air objectives have a maximum NA of 0.9 but for applications where spatial resolution is critical, immersion objectives can be used to obtain a higher NA. Here, 1 an immersion fluid with a higher refractive index than air (1) is placed between the front lens of the objective and a coverslip/sample where in normal objectives air would be. The two most commonly used fluids are water with a refractive index of 1.3, and oil which has a refractive index of approximately 1.5 (dependent on oil type). Water immersion objective have particular use in confocal Raman microscopy for the study of live cells in cell media, whilst oil objectives can be useful for depth studies.
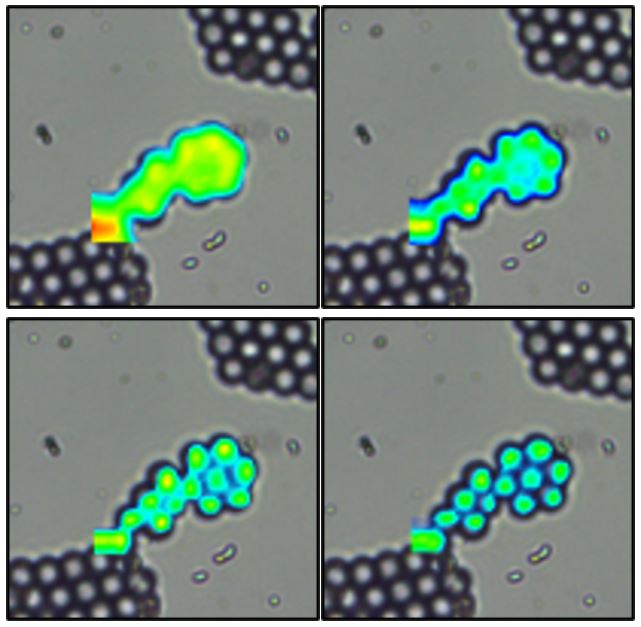
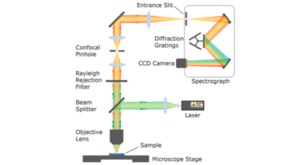
The highest lateral spatial resolution can only be achieved using a confocal Raman microscope. Confocal Raman microscopes utilise a pinhole that is used to reject out of focus light from detection. Figure 1 highlights the improvement in spatial resolution of polystyrene beads by narrowing the pinhole diameter of the Edinburgh Instruments RM5 Raman Microscope.
Figure 1: polystyrene beads mapped on the RM5 Raman Microscope with varying pinhole diameters A) 2 mm B) 100 µm C) 50 µm D) 25 µm.
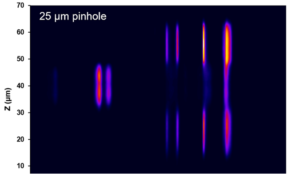
The axial spatial resolution (Z axis) is proportional to λ/NA2 and like the lateral resolution it improves with decreasing wavelength and higher NA objectives. However, the main parameter that controls the axial resolution is the confocal pinhole diameter, the narrower the pinhole the better the axial resolution. At the narrowest pinhole diameters a depth resolutions on the order of 1 µm can be achieved in ideal samples. More information about the relationship between pinhole diameter and resolution can be found in our Spectral School tutorial on the role of the pinhole in Raman microscopy.
The video below shows an example of the axial information that can be obtained with a confocal Raman microscope. The 3D Raman map was reveals the different material layers of a transdermal drug delivery patch. The different colours show the identification and location of PET (red), PET/PIB (pink), PE (blue) plastic and the active pharmaceutical ingredient (green).